-
Research Article
-
A French Cartographer Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d’Anville: His Geography and The Korean Peninsula and Surrounding Areas Depicted in His East Asian Maps
프랑스 지도학자 장 밥티스트 부르귀뇽 당빌의 지리학과 동아시아 지도 속에 표시된 한반도와 주변 지역
-
In-Chul Jung
정인철
- This paper analyzes the geography of French cartographer Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d’Anville and the geographic information depicted on the Korean Peninsula and surrounding …
이 논문은 프랑스 지도학자 장 밥티스트 부르귀뇽 당빌의 지리학과 그가 제작한 동아시아 지도 속 한반도와 주변 지역에 표시된 지리정보를 분석한 연구이다. 먼저 …
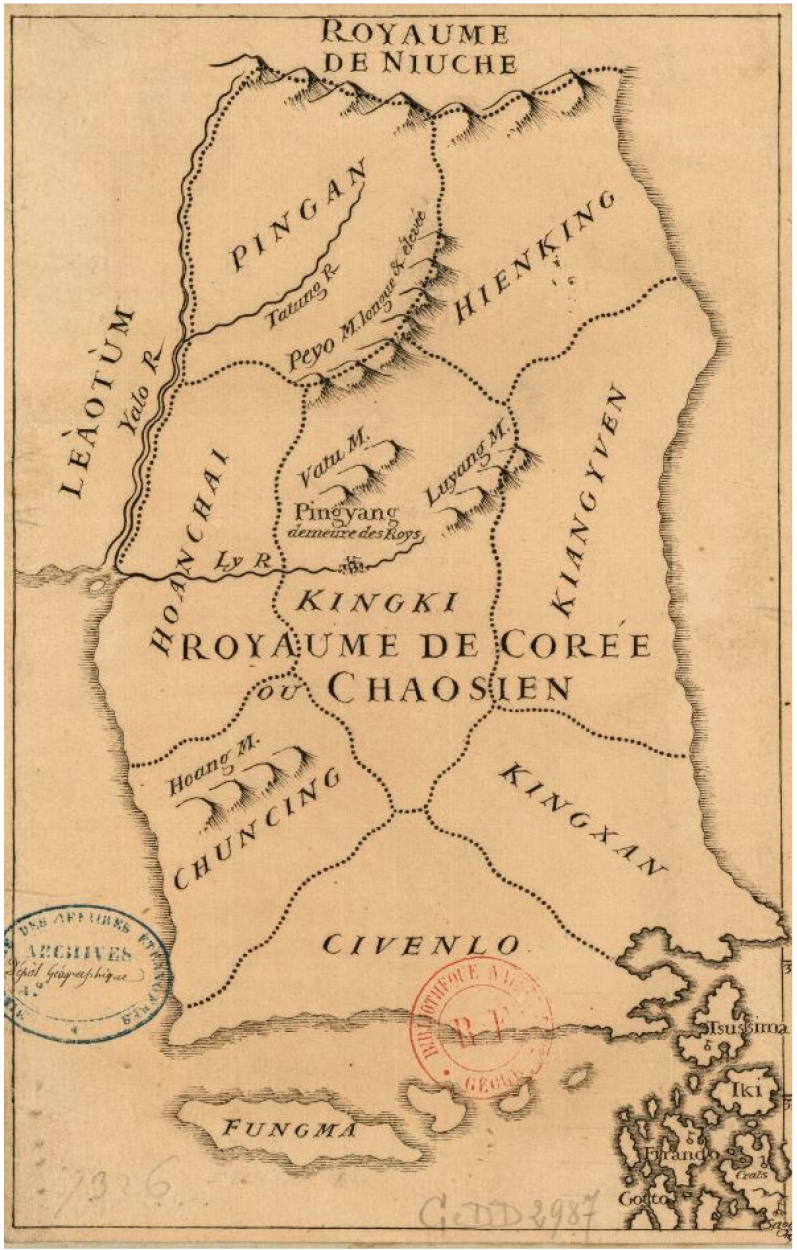
- This paper analyzes the geography of French cartographer Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d’Anville and the geographic information depicted on the Korean Peninsula and surrounding regions within his East Asian maps. To this end, it first systematically examines d’Anville’s geographical methodology. Departing from the existing speculative tradition, D’Anville significantly enhanced the accuracy of positional data by combining empirical evidence with mathematical calculations. His geography attempted a scientific discussion of the Earth’s form, seeking to treat uncertain geographical knowledge scientifically. Furthermore, it compares and analyzes the geographical information of the Korean Peninsula and surrounding regions, focusing on the three East Asian maps produced by D’Anville. By analyzing the changes in the depiction of the northern mountain ranges of Joseon, the border between Joseon and Qing China, and the labeling of place names in these maps, we clarified the impact of D’Anville’s perception of the Korean Peninsula on the Western cartographic tradition. Furthermore, we revealed that in the 1752 “Map of Asia Including Parts of China and Tartary” the Romanization system was significantly revised to reflect Chinese phonetic characteristics and ensure consistency in transliteration.
- COLLAPSE
이 논문은 프랑스 지도학자 장 밥티스트 부르귀뇽 당빌의 지리학과 그가 제작한 동아시아 지도 속 한반도와 주변 지역에 표시된 지리정보를 분석한 연구이다. 먼저 이를 위해 당빌의 지리학적 방법론을 체계적으로 고찰했다. 당빌은 기존의 추측적 전통에서 벗어나, 경험적 자료와 수학적 계산을 결합하여 위치 자료의 정확성을 획기적으로 높였다. 그의 지리학은 지구 형태에 대한 과학적 논의를 시도하여 불확실한 지리 지식을 과학적으로 다루려 했다. 그리고 당빌이 제작한 세 장의 동아시아 지도를 중심으로 한반도와 주변 지역의 지리정보를 비교·분석하였다. 이들 지도 속에 나타난 조선 북부 산맥, 조·청 경계, 지명 표기의 변화를 분석하여 당빌의 한반도 인식과 서구 지도학 전통에 미친 영향을 규명하였다. 연구 결과 1752년 「중국과 달단 일부를 포함하는 아시아 지도」에서는 중국어 음운적 특징을 반영하고 음차의 일관성을 확보하기 위해 로마자 표기 체계를 대폭 수정한 사실을 밝혀냈다.
-
A French Cartographer Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d’Anville: His Geography and The Korean Peninsula and Surrounding Areas Depicted in His East Asian Maps
-
Research Article
-
Map Indices for Large Scale Antarctic Maps
남극 대축척 지도 제작을 위한 도엽 체계 설정에 관한 연구
-
Jae-joon Jeong
정재준
- Korea operates two Antarctic stations, King Sejong and Jang Bogo, conducting various scientific research activities and has a plan to build a …
우리나라는 남극 세종 기지와 장보고 기지를 운영하며 다양한 과학 연구 활동을 수행하고 있으며, 남극 내륙 고위도 지역에 제3기지 건설을 계획하고 있다. 우리나라의 …
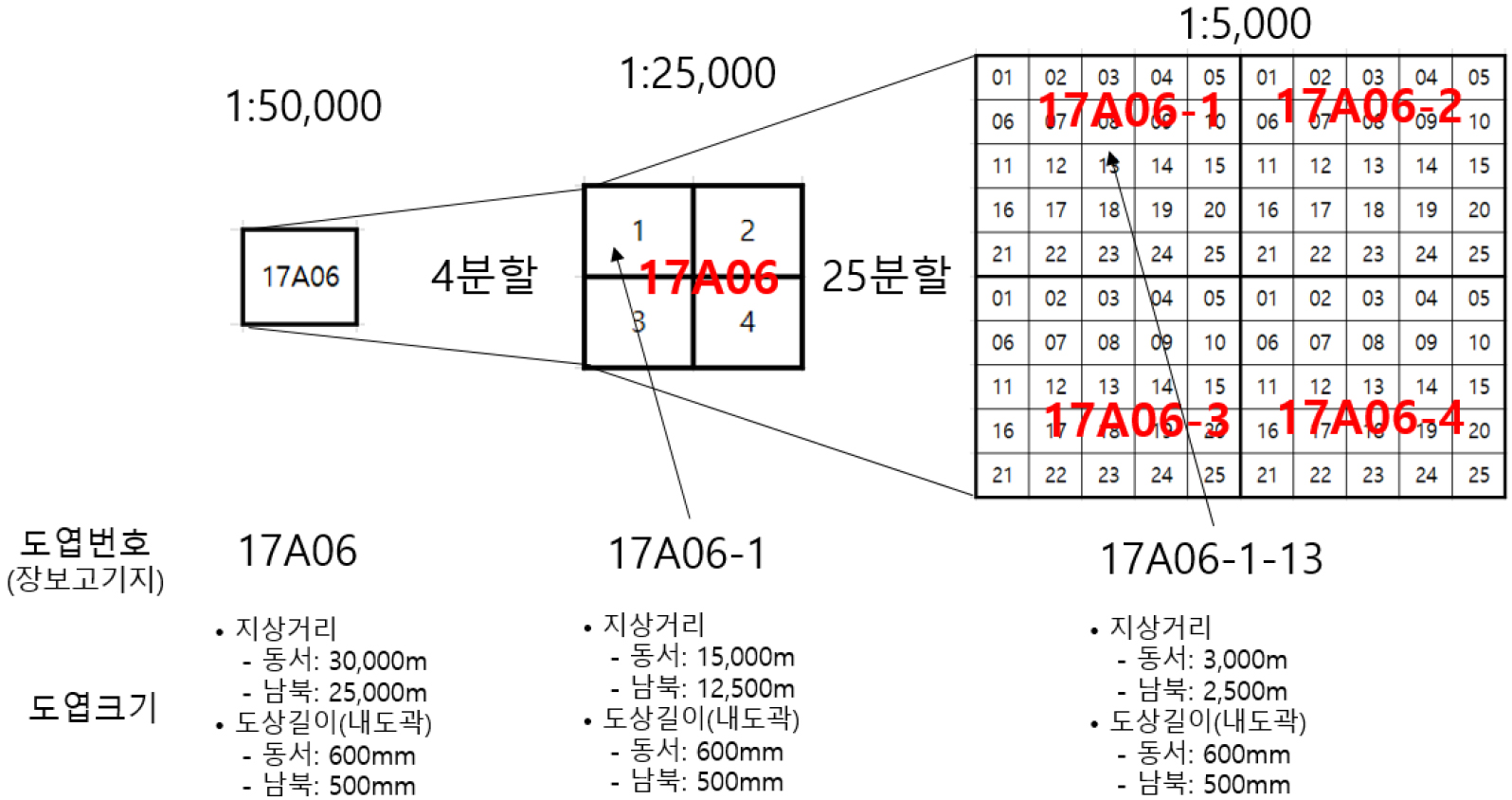
- Korea operates two Antarctic stations, King Sejong and Jang Bogo, conducting various scientific research activities and has a plan to build a third station in the high-latitude interior of Antarctica. The National Geographic Information Institute (NGII) has produced large-scale maps of the areas surrounding King Sejong and Jang Bogo Stations since 2009 and plans to produce maps of the research area, the third station, and the K-Route area. Large-scale maps require a specific map indices system, with map sheets dividing system and map sheet numbering system by scale. However, currently produced large-scale maps lack this. This study addressed these issues by establishing criteria for map indices system based on three aspects: rectangular coordinates division, output paper size and location identification by map sheet number. Based on these criteria, this study proposed a new map indices system applicable throughout Antarctica.
- COLLAPSE
우리나라는 남극 세종 기지와 장보고 기지를 운영하며 다양한 과학 연구 활동을 수행하고 있으며, 남극 내륙 고위도 지역에 제3기지 건설을 계획하고 있다. 우리나라의 지도 제작 기관인 국토지리정보원은 2009년 이후 현재까지 세종 기지와 장보고 기지 주변의 대축척 지도를 제작하였으며, 남극 연구 지역, 제3기지와 K루트 주변에 대해 지도를 제작할 계획이다. 대축척 지도는 일정한 기준에 의해 축척별로 도엽이 분할되고 도엽번호가 부여되는 등 명확한 도엽 체계를 갖추어야 하지만 현재 제작된 대축척 지도는 그렇지 못한 것이 현실이다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 점에 착안하여 ‘직각좌표에 의한 분할’, ‘출력 용지 크기를 고려한 분할’, ‘도엽번호에 의한 위치 파악 및 축척별 포섭 관계’ 3가지 측면을 고려한 도엽 분할 기준을 설정하고, 설정된 기준에 따라 축척별 도엽 체계를 마련하여 남극 전역에 적용할 수 있는 새로운 도엽 체계를 제시하였다.
-
Map Indices for Large Scale Antarctic Maps
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Early Nautical Charts of the Korean Peninsula Compiled by the Japanese Hydrographic Office in the Late Nineteenth Century
19세기 후반 일본 수로국 작성 ‘초기 한반도 해도’ 연구
-
Jong-Geun Kim
김종근
- This study analyzes the background and cartographic characteristics of the “Early nautical charts of the Korean Peninsula” produced by the Japanese Hydrographic …
본 연구는 19세기 후반 일본 수로국이 작성한 ‘초기 한반도 해도’를 대상으로 그 제작 배경과 지도학적 특징을 분석하였다. 연구 대상은 1875년부터 1885년까지 일본 …
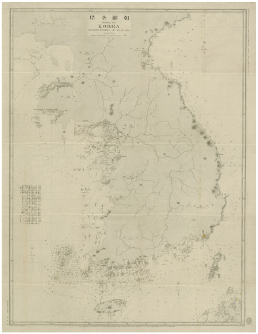
- This study analyzes the background and cartographic characteristics of the “Early nautical charts of the Korean Peninsula” produced by the Japanese Hydrographic Office in the late nineteenth century. The research scope covers 23 charts (30 sheets) created between 1875 and 1885. The findings reveal the establishment and transformation of Japan’s hydrographic institutions and confirm that Article 7 of the 1876 Treaty of Ganghwa and its Appendix 9 provided the legal basis for Japan’s coastal surveys of Korea. Notably, this study identifies that, even before the treaty, Japan had conducted unauthorized surveys and produced charts of Busan, Ungcheon Bay, Jemulpo, and the Yeomha area of Ganghwa Island. Furthermore, the analysis demonstrates that the early charts reflected military objectives such as naval operations and economic aims such as the exploration of open ports. It is also confirmed that the legend items prescribed in the “Japanese Naval Chart Signs and Abbreviations” were incorporated into the charts. By the 1880s, Japan had already moved beyond simple replication of Western charts and was producing nautical charts based on its own techniques, with the waters surrounding the Korean Peninsula serving as one of the key survey targets.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 19세기 후반 일본 수로국이 작성한 ‘초기 한반도 해도’를 대상으로 그 제작 배경과 지도학적 특징을 분석하였다. 연구 대상은 1875년부터 1885년까지 일본 해군 수로국이 제작한 해도 23종 30매이다. 이 연구를 통해 일본 수로국의 성립과 변천 과정이 파악되었고, 조일수호조규(1876) 제7관 및 부록 제9관이 일본의 한반도 해안 측량을 합법화하는 근거가 되었음을 확인하였다. 특히 조약 체결 이전에도 일본이 부산항뿐 아니라 웅천만, 제물포, 강화도 염하 등에서 불법적으로 측량하여 해도를 제작한 사례가 존재함을 최초로 밝혀냈다. 아울러 ‘초기 한반도 해도’는 해군 작전 수행과 개항장 탐색이라는 군사적·경제적 목적을 반영하여 작성된 것임을 확인하였다. 또한 해도에 기재된 내용은 ‘일본 해군 해도식’의 범례 사항이 반영되어 있음을 확인하였다. 이를 통해 1880년대에 이미 일본이 서구 해도를 단순 복제하는 수준을 넘어 독자적 기술을 바탕으로 해도를 제작하고 있었으며, 한반도 주변 해역이 중요한 조사 대상지 중 하나였음을 알 수 있다.
-
A Study on the Early Nautical Charts of the Korean Peninsula Compiled by the Japanese Hydrographic Office in the Late Nineteenth Century
-
Research Article
-
Development of the Guidelines for Local Government Satellite Imagery Utilization and its Implications
지방자치단체 위성영상 활용을 위한 가이드라인 개발 및 그 함의
-
Eunmi Chang · Jiwon Kim · Seonhee Hong · Yeolim Son
장은미 · 김지원 · 홍선희 · 손여림
- While local governments are increasingly utilizing diverse imagery data, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and drone images, practical guidelines for their comprehensive …
지방자치단체가 위성영상, 항공사진, 드론 영상 등 다양한 영상 자료를 활용하는 사례가 증가하고 있으나, 이를 포괄적으로 관리하고 효율적으로 활용하기 위한 실질적인 가이드라인은 현재 …
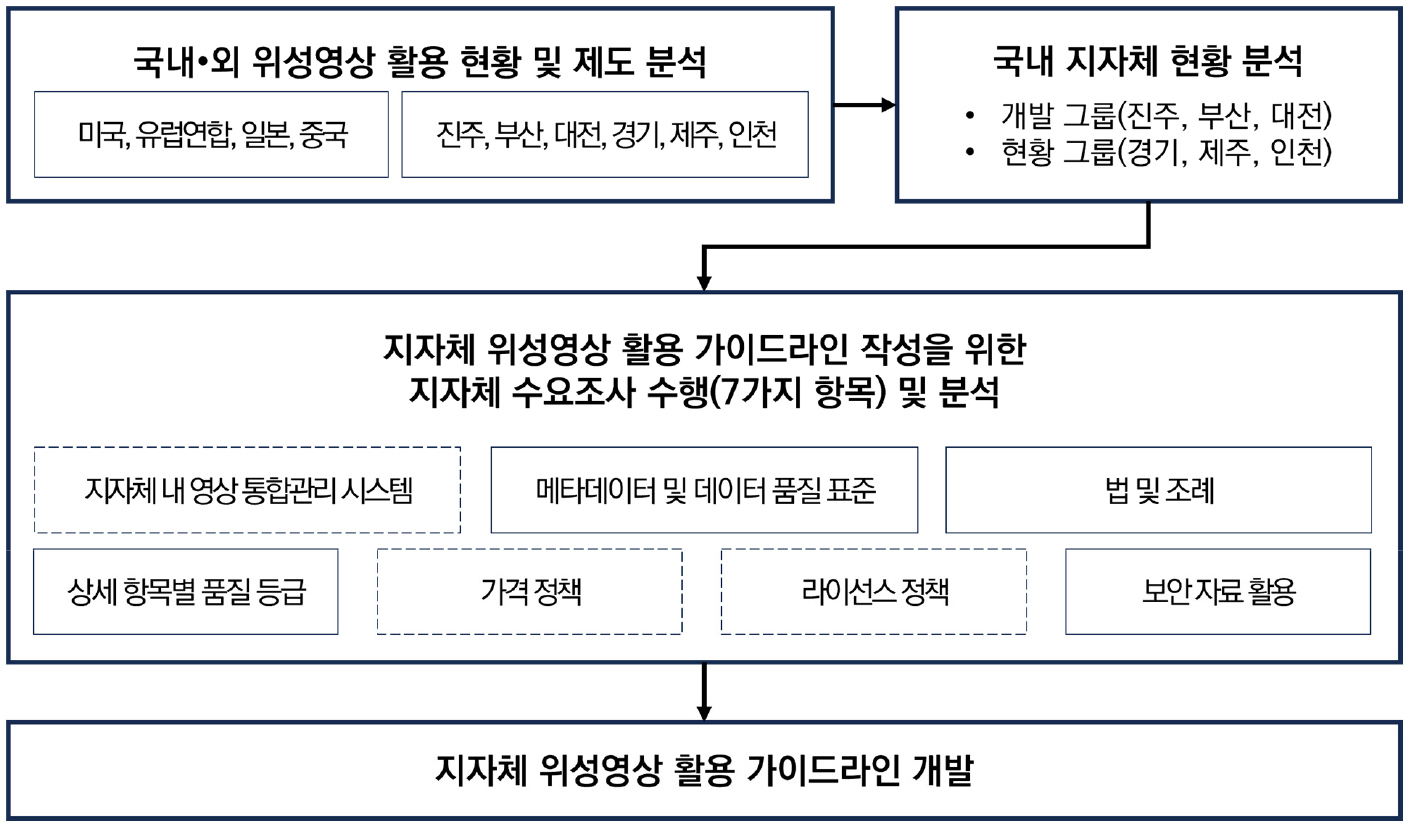
- While local governments are increasingly utilizing diverse imagery data, including aerial photography, satellite imagery, and drone images, practical guidelines for their comprehensive management and efficient utilization are currently lacking. Against this background, this study aims to identify the necessity for guidelines to facilitate the effective use of various types of imagery data and to develop a framework. To achieve this, the research methodology involved reviewing the current legal frameworks governing international satellite data policies, which play a pivotal role in the supply and demand of satellite imagery, as well as examining domestic developments related to the space industry and satellite information. The analysis revealed that despite ongoing active technological developments at various satellite centers, local governments will require specific, documented guidelines addressing critical issues such as pricing, security, quality, and integrated management, as identified by this research, to ensure the effective utilization of imagery data.
- COLLAPSE
지방자치단체가 위성영상, 항공사진, 드론 영상 등 다양한 영상 자료를 활용하는 사례가 증가하고 있으나, 이를 포괄적으로 관리하고 효율적으로 활용하기 위한 실질적인 가이드라인은 현재 부재한 실정이다. 이러한 배경에서 본 연구는 다양한 유형을 가진 영상 자료의 효과적인 활용을 촉진하기 위한 가이드라인의 필요성을 규명하고 프레임워크를 개발하고자 수행되었다. 이를 위해 연구 방법론으로서 위성영상 수급의 핵심적 역할을 하는 국제 위성 데이터 정책의 현행 법적 프레임워크를 검토하고, 국내의 우주산업 및 위성정보 관련 내용을 살펴보았다. 분석 결과, 다수의 위성 센터에서 위성정보를 손쉽게 활용하기 위한 기술 개발이 활발히 진행되고 있음에도 불구하고, 지방자치단체의 효율적인 영상 자료 활용을 위해서는 본 연구를 통해 도출된 바와 같이 가격, 보안, 품질, 통합 관리와 같은 주요 쟁점들을 포괄하는 구체적인, 문서화된 가이드라인 마련이 필요하다는 것을 말해준다.
-
Development of the Guidelines for Local Government Satellite Imagery Utilization and its Implications
-
Research Article
-
Analyzing Changes in Suburban Decline in the Seoul Metropolitan Area: Focusing on Population-Housing Double Aging
수도권 교외지역 쇠퇴의 변화 분석: 인구·주택 이중노후화를 중심으로
-
Youjin Hong · Jungyeop Shin
홍유진 · 신정엽
- This study empirically examines suburban decline by analyzing “double ageing,” a condition in which both population ageing and housing ageing progress simultaneously, …
본 연구는 교외지역 쇠퇴 현상을 실증적으로 규명하기 위하여 인구 고령화와 주택 노후화가 동시에 진행되는 ‘이중노후(double ageing)’를 1km 격자 단위에서 분석하였다. 2000-2020년 동안 …
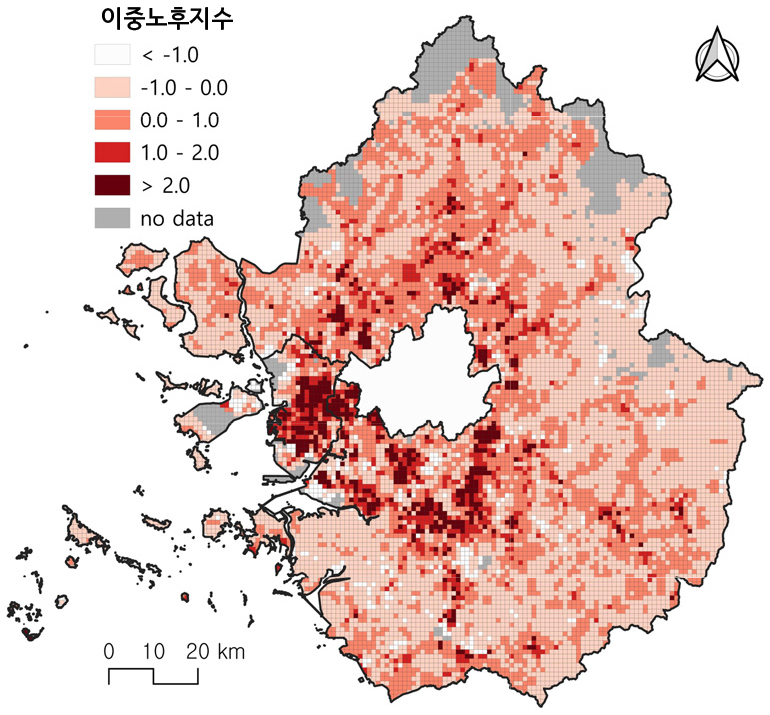
- This study empirically examines suburban decline by analyzing “double ageing,” a condition in which both population ageing and housing ageing progress simultaneously, at a 1 km grid scale. The Double Ageing Index (DAI) was constructed by combining the Z-standardized compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the elderly population ratio and the Z-standardized change in average housing age between 2000 and 2020. Using the DAI, the study first identified grids exhibiting double ageing and then examined their population and housing characteristics. In addition, Getis-Ord' G* statistics and ring(distance)–direction(sector) analyses were applied to capture spatial clustering patterns and directional diffusion of double ageing. The results indicate that double ageing is concentrated in the inner suburban belt within 20km of Seoul’s administrative boundary, and is particularly associated with large-scale apartment complexes supplied in the 1990s. This suggests that these areas have undergone rapid double ageing due to structural similarities in housing development periods and household composition. By contrast, outer low-density areas show relatively low DAI values, despite high absolute levels of ageing, because their rates of change remain modest. Through fine-scale, grid-based spatial analysis, this study provides empirical evidence of suburban decline grounded in double ageing and highlights the need for a paradigm shift in suburban policy frameworks.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 교외지역 쇠퇴 현상을 실증적으로 규명하기 위하여 인구 고령화와 주택 노후화가 동시에 진행되는 ‘이중노후(double ageing)’를 1km 격자 단위에서 분석하였다. 2000-2020년 동안 노인인구 비율 증가율과 평균주택연령 변화량을 Z-표준화하여 결합한 이중노후지수(DAI)를 바탕으로, 이중노후가 나타나는 격자들에 대해 인구 및 주택 특성을 검토하였다. 또, Getis-Ord' G*, 거리(고리)·방위(섹터) 분석을 적용해 공간적 집적성과 확산 경향을 확인하였다. 분석 결과, 이중노후는 서울 경계 20km 이내의 내부 교외지역에 집중되었으며, 특히 1990년대 대규모 아파트 공급지와 연계되는 것으로 나타났다. 이는 해당 지역들이 동일 시기에 형성된 주택과 세대구성의 구조적 유사성 때문에 인구·주택의 이중노후화가 급격히 나타났음을 보여준다. 반면 외곽 저밀도 지역은 절대적 노후 수준이 높음에도 변화율이 낮아 이중노후지수는 작게 나타났다. 본 연구는 격자 기반 미세공간 분석을 통해 교외지역의 이중노후화에 토대한 쇠퇴 양상을 실증적으로 규명하였으며, 향후 교외지역 정책 패러다임의 전환이 이루어져야 함을 제시하였다는 의의를 가진다.
-
Analyzing Changes in Suburban Decline in the Seoul Metropolitan Area: Focusing on Population-Housing Double Aging
-
Research Article
-
Exploration of Spatial Accessibility of Lifelong Education Service in terms of Regional Characteristics: Case of Daejeon-si, Cheonan-si, and Hongseong-gun
지역 특성에 따른 평생교육 서비스의 공간 접근성 탐색: 대전광역시, 천안시, 홍성군을 사례로
-
Jungyeop Shin · Asoo Choi
신정엽 · 최아수
- In recent years, increasing interest in lifelong education across all generations has been accompanied by a growth in scholarly research. As a …
최근 전 세대에 걸친 평생교육에 대한 관심과 더불어, 평생교육에 관한 연구가 수행되어 왔다. 공공성 측면을 지닌 평생교육은 가능한 한 쉽게 접근하고 편리하게 …
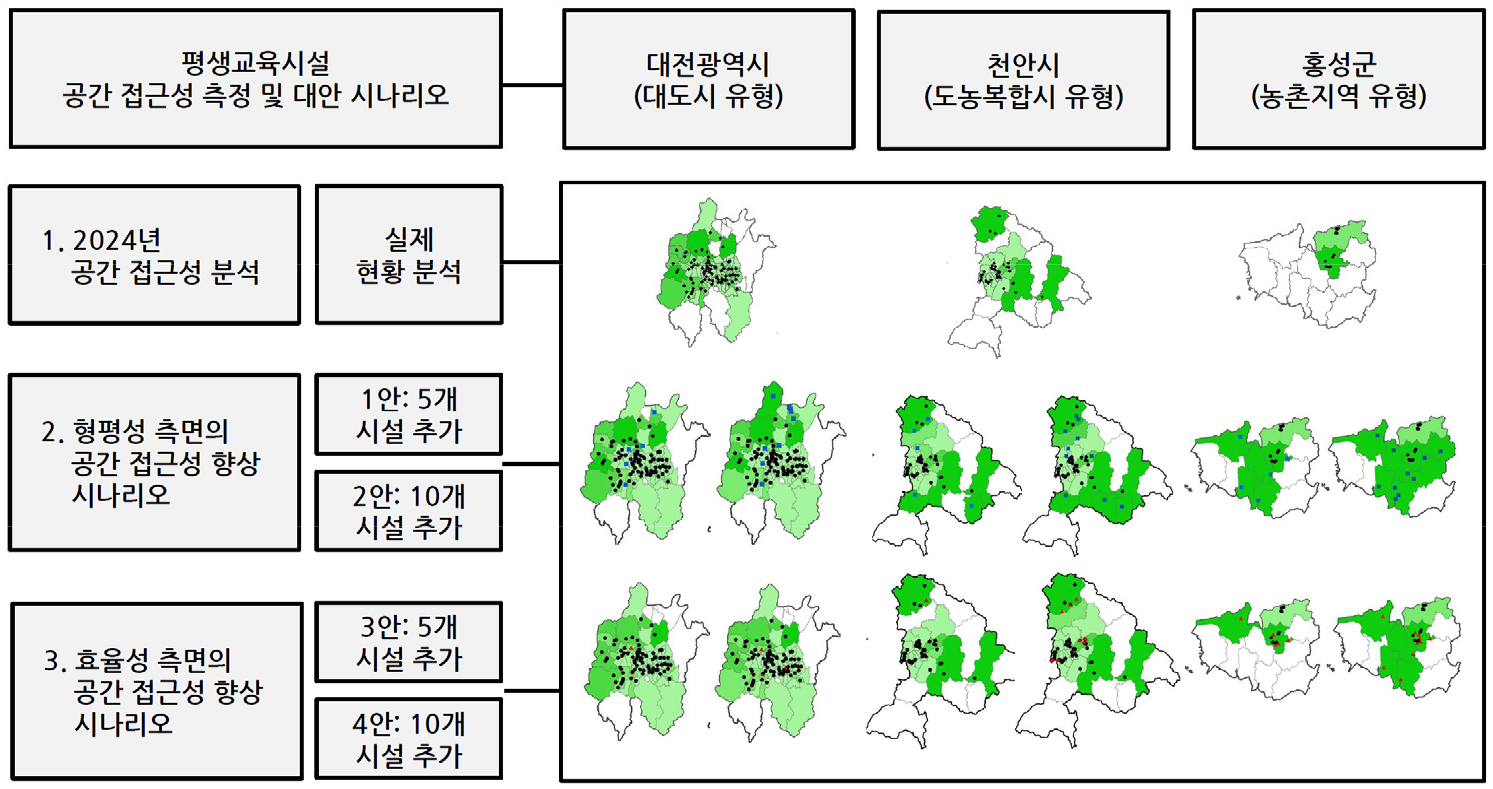
- In recent years, increasing interest in lifelong education across all generations has been accompanied by a growth in scholarly research. As a public service, lifelong education must be both easily accessible and conveniently available to all individuals; thus, spatial accessibility emerges as a critical factor in its provision. This paper conducts an empirical case analysis to examine spatial accessibility to lifelong education services. Recognizing that spatial accessibility is likely to vary according to regional characteristics—such as metropolitan, urban–rural mixed, and traditional rural region. Further, the research investigates how the addition of new lifelong education facilities influences accessibility within these distinct regional contexts. Spatial accessibility was measured using the Two-Step Floating Catchment Area (2SFCA) method in three study regions: the Daejeon Metropolitan region, Cheonan-si, and Hongseong-gun. In addition, alternative facility allocation scenarios by adding five and ten new facilities in each region were explored from both equity and efficiency perspectives. The findings indicate that, relative to potential demand populations, Cheonan and Hongseong exhibit slightly higher overall spatial accessibility than the Daejeon Metropolitan City. The analysis also reveals a clustered distribution of lifelong education facilities in all three regions, resulting in high accessibility around these clusters but lower accessibility in peripheral areas. Under the alternative location scenarios, the equity analysis demonstrates significant improvements in spatial accessibility in Cheonan and Hongseong, whereas Daejeon experiences little change. The efficiency analysis shows little change in Daejeon and Cheonan but identifies a considerable improvement in Hongseong. Taken together, these results confirm that spatial accessibility to lifelong education services differs significantly across regional types and that both equity and efficiency considerations yield distinct implications for facility allocation strategies.
- COLLAPSE
최근 전 세대에 걸친 평생교육에 대한 관심과 더불어, 평생교육에 관한 연구가 수행되어 왔다. 공공성 측면을 지닌 평생교육은 가능한 한 쉽게 접근하고 편리하게 서비스를 받을 필요가 있으며, 이와 관련하여 공간 접근성이 매우 중요하다. 본 연구는 평생교육 서비스의 공간 접근성에 대한 실증적 사례분석을 수행하였다. 특히, 대도시, 도농복합시, 농촌지역의 지역 특성에 따라 평생교육 서비스의 공간 접근성 차이가 있을 것이며, 기존 평생교육 시설에 추가로 입지시키는 경우 지역의 공간 접근성이 어떻게 변화되는지를 비교, 분석하고자 하였다. 본 연구는 대전광역시, 천안시, 홍성군을 사례로 2SFCA 기법을 활용하여 공간 접근성을 측정하였으며, 또한 입지 대안으로 형평성, 효율성 측면에서 각 지역에 평생교육 시설을 5개, 10개를 추가한 경우의 공간 접근성을 비교하였다. 분석 결과, 평생교육 시설 대비 잠재적 수요 인구 측면에서 대도시인 대전광역시보다 천안시, 홍성군의 공간 접근성이 약간 높았다. 그리고 세부 공간구조 측면에서 세 지역 모두 평생교육 시설이 집적되어 있으며 이곳을 중심으로 공간 접근성이 높게 나타나지만, 다른 외곽 지역의 공간 접근성은 낮은 것으로 나타났다. 평생교육 시설의 추가 입지 대안의 경우, 형평성 측면의 분석에서는 천안시, 홍성군에서 공간 접근성이 향상되었지만, 대전광역시는 기존과 큰 변화가 없었다. 효율성 측면의 분석에서는 대전광역시, 천안시의 경우 공간 접근성의 큰 차이가 없는 반면, 홍성군은 공간 접근성이 향상되었다. 이러한 다양한 지역 특성에서의 평생교육 시설의 공간 접근성 측정 및 비교와 형평성, 효율성 측면의 대안 분석 결과를 토대로, 평생교육 서비스는 실제로 지역 특성에 따라 공간 접근성의 차이가 있음을 확인하였다.
-
Exploration of Spatial Accessibility of Lifelong Education Service in terms of Regional Characteristics: Case of Daejeon-si, Cheonan-si, and Hongseong-gun
-
Research Article
-
Estimating Seasonal Green View Index via Fusion of Sentinel-2 NDVI Time Series and High-Resolution Vegetation Mask
NDVI와 고해상도 식생 마스크를 활용한 계절별 Green View Index 추정
-
Seungjoo Ha · Youngok Kang
하승주 · 강영옥
- The Green View Index (GVI) quantifies the visibility of greenery from a pedestrian perspective and is widely used to assess walking environments. …
Green View Index(GVI)는 보행자 관점의 녹지 가시성을 정량화하는 지표로 보행 환경 평가에 널리 활용된다. 최근 보행자 시점의 시각적 녹지 중요성이 대두되며 녹색이 …
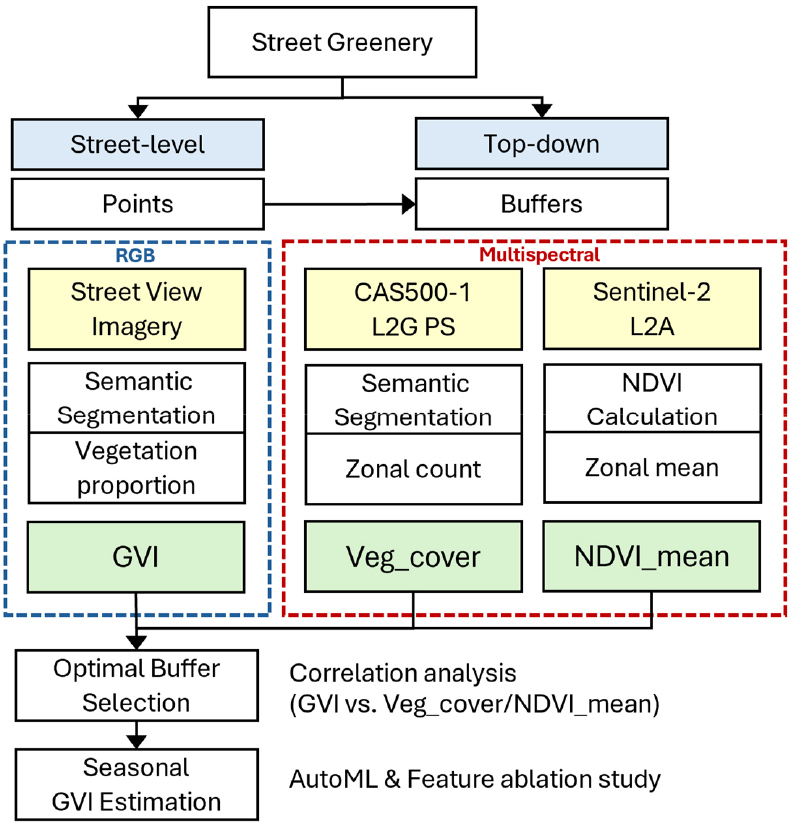
- The Green View Index (GVI) quantifies the visibility of greenery from a pedestrian perspective and is widely used to assess walking environments. As the importance of pedestrian-view visual greenery has grown, there is a need to analyze seasonal diversity beyond the greenery-rich summer months. GVI is typically derived from street-view imagery; however, such imagery is often captured intensively in specific seasons and updated at roughly annual intervals, limiting its ability to reflect seasonal variability. This study proposes a framework for estimating the seasonal Green View Index (GVI) by fusing a Sentinel-2 NDVI time series with a high-resolution vegetation mask. Using the proposed approach, which incorporates seasonal NDVI, high-resolution vegetation cover, and cyclical month encoding, we achieved strong performance (R2 = 0.819, MAE = 0.038, r = 0.906). Improvements were especially pronounced in spring and autumn, when vegetation vigor is low but visually perceived greenery is salient. These results demonstrate that augmenting traditional satellite-based greenness metrics (NDVI) with high-resolution structural vegetation information and acquisition month substantially enhances the estimation of pedestrian-view GVI and its seasonal variability.
- COLLAPSE
Green View Index(GVI)는 보행자 관점의 녹지 가시성을 정량화하는 지표로 보행 환경 평가에 널리 활용된다. 최근 보행자 시점의 시각적 녹지 중요성이 대두되며 녹색이 많은 여름 외에도 녹지의 계절별 다양성을 분석할 필요성이 제기되고 있다. GVI는 주로 거리영상을 통해 생성되는데, 거리영상은 특정 계절에 집중적으로 촬영되고, 영상 갱신이 약 1년 주기로 이뤄지므로 계절에 따른 변동성을 반영하는 데에 한계가 있다. 본 연구는 위성영상에 기반한 NDVI 시계열과 고해상도 식생 마스크를 결합하여 GVI의 계절별 다양성을 추정하는 프레임워크를 제안한다. 제안한 방법론으로 GVI를 추정할 때, 계절별 NDVI, 고해상도 식생 커버, 월 변수를 포함할 경우 R2 = 0.819, MAE = 0.038, Pearson’s r = 0.906의 높은 성능을 달성하였다. 특히 식생 활력이 낮으나 시각적 식생이 두드러지는 봄·가을 GVI 추정 성능이 크게 향상되었다. 이는 전통적인 위성 기반 녹지 모니터링 지표인 NDVI에 고해상도 식생 마스크와 월 정보를 추가함으로써 보행자 시각 GVI 추정 성능을 유의하게 향상시킴을 입증한 것이라 할 수 있다.
-
Estimating Seasonal Green View Index via Fusion of Sentinel-2 NDVI Time Series and High-Resolution Vegetation Mask
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Cartographic Association
Journal of the Korean Cartographic Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Cartographic Association
Journal of the Korean Cartographic Association








